The method is based on pneumatic conveying of the moulding aggregate into the core box or a moulding box. Compressed air is used for this purpose, normally at the standard mains pressure of 500 ÷ 700 kPa. Before the compaction process, the core box, or the moulding box, is pushed up against the blowing head by elevating the machine table by its pneumatic cylinder. The air is introduced directly at the mains pressure through a quick acting valve into the moulding aggregate reservoir. When the main air valve is opened, fluidized mixture of the air and moulding aggregate is injected into the vented core box at a high velocity. When the aggregate impacts on a solid surface in the core or a moulding box, its kinetic energy is used for compaction, and the air being exhausted through filtered vents. The moulding aggregate entrained by the air flow can move through an indirect path, thereby filling the complex shapes. The condition for proper filling of the core (mould) is good flowability and permeability of the used mixture. The aggregates bonded with clay and sodium silicate are not suitable for blowing. The degree of compaction is not high; this method is used with the second generation moulding aggregates, where the resulting strength is achieved by curing the binder.
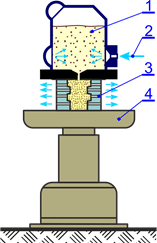
Core blower;
1 – aggregate reservoir, 2 – compressed air inlet, 3 – core box with vents, 4 – machine table