The principle of impact compaction, known also as pulse/impulse compaction or dynamic compaction, consists in pouring the moulding aggregate onto the pattern plate, and its subsequent compaction by a shock wave. High velocity and high acceleration are the characteristic features of the shock wave; the absolute pressure value must not be extremely high. At high speeds, solids behave like liquids and are subject to the laws of hydrodynamics. For this reason, the shock wave propagates without a significant restriction also through a thick layer of the moulding aggregate until it hits the pattern plate. The energy of the shock wave accelerates and hurls the aggregate grain against the pattern plate, where its compaction takes place owing to inertia forces. At the place of impact, the pressure values are substantially higher than the pressure of air or the gas acting on the surface of the moulding aggregate. Fluidization of the moulding aggregate under the rapid flow of air or gas reduces friction, and a uniformly compacted mould is produced. Moreover, the front of the pressure wave is partially reflected from the pattern plate and returns to the back of the mould again – a secondary compaction of the moulding aggregate occurs. The favourable density distribution in the compacted mould is achieved, where the maximum density is at the pattern face. Depending on the way of inducing a shock wave, there are two variants of this method:
- Gas-Impact – shock wave is induced by explosive gas combustion,
- Air-Impact – shock wave is induced by rapid expansion of large volume of pre-compressed air.
Gas-Impact
The older of the two methods is the Gas-Impact method developed by Georg Fisher, the Swiss Company in the early 1980s. The shock wave used for the moulding aggregate compaction is induced by exothermic combustion of a mixture of gas (natural gas, methane or propane) and air.
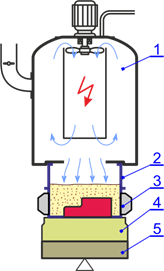
Principle of Gas-Impact pulse compaction method;
1 – pressure chamber, 2 – filling frame, 3 – moulding box, 4 – damping pad, 5 – machine table.
Air-Impact
The principle of this method differs from the previous one only in the shock wave produced by a rapid expansion of large volume of pre-compressed air released by one or more valves with extremely fast opening.
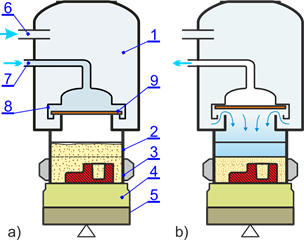
Principle of Air-Impact pulse compaction method;
a) pressurizing of the air reservoir, b) shock wave formation at the moment of diaphragm valve opening;
1 – air reservoir, 2 – filling frame, 3 – moulding box, 4 – damping pad,
5 – machine table, 6 – compressed air inlet, 7 – control pressure of valve,
8 – large capacity quick acting valve, 9 – diaphragm of the valve